While regular exercise and a healthy diet is recognized as the ideal way to maintain a normal , there are some individuals for whom weightloss surgery or bariatric surgery is the only option remaining.
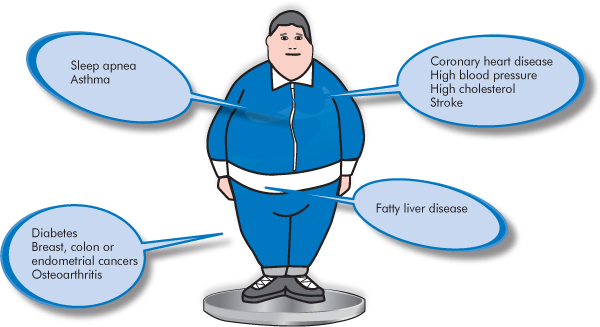
People who are morbidly obese and have tried and failed to lose using conventional methods are turning to surgical weight loss as a solution. Bariatric surgery is recommended only for people with severe obesity; that is, with a body mass index above 40.
Weight loss surgery is also offered to people with BMI between 35 and 40 if they also suffer from obesity-related health problems such as diabetes or sleep apnea.
Surgical Weight Loss Options
When diet, exercise or loss medications are not enough to reach and maintain a healthy weight, people who suffer from severe obesity can resort to a number of surgical options for loss:
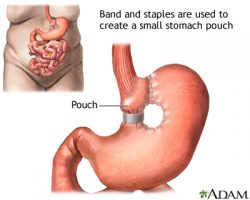
Gastric Bypass. A gastric bypass allows you to lose in two ways: first, by limiting the amount of food ingested and second, by reducing the amount of nutrients you absorb from your food. This is done by creating a smaller stomach pouch which is attached to the lower part of the small intestine. The smaller stomach holds less food so you feel full sooner. Also, fewer calories are absorbed because the food bypasses a portion of the stomach and small intestine.
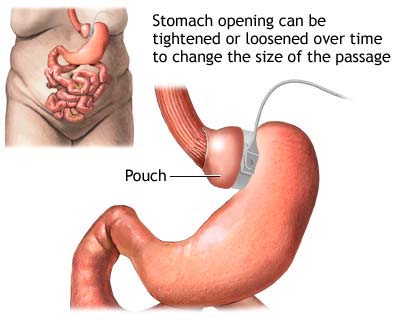
Lap Banding. This surgical weight loss procedure uses an adjustable band inserted in the stomach to give a feeling of fullness and limit the amount of food consumed. The lap band can be tailor-made for the patient. It is also adjustable after surgery so that you can eat more or less food as needed.
Gastric sleeve. This type of stomach reduction surgery is one of the newer options for surgical loss. It makes the stomach smaller by removing up to 85% of the stomach, leaving only a narrow, banana-shaped tube. With a smaller stomach, you will feel full even with less food. This loss surgical procedure is safer compared to gastric bypass because it does not rearrange the digestive anatomy. It may also be safer than lap banding since no foreign objects are introduced into the digestive system.
Benefits of Surgical Weight Loss
Quick and effective loss. Most patients start to lose immediately following surgery. In general, patients lose rapidly within 6 months to one year. Weight loss often continues until two years after the surgical procedure., and few patients regain it.
Improved health conditions. A number of studies found that loss surgery can return blood sugar levels to normal in patients with type 2 diabetes. There is also an improvement in obesity-related health conditions such as sleep apnea and high blood pressure.
Psychosocial adjustment. As patients reach a more normal , their self-esteem and self-image also improve and they are better able to function in society.
Risks of Surgical Weight Loss
Side effects. Patients may experience vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, and dizziness.
Nutritional deficiencies. Surgical loss may be accompanied by nutritional deficiencies including anemia and osteoporosis.
Complications. After loss surgery, some patients may suffer from complications such as abdominal hernias, infections, gallstones, or breakdown of the staple line used to make the stomach smaller.
Lifestyle changes. Bariatric surgery often requires permanent lifestyle changes for significant and lasting loss.