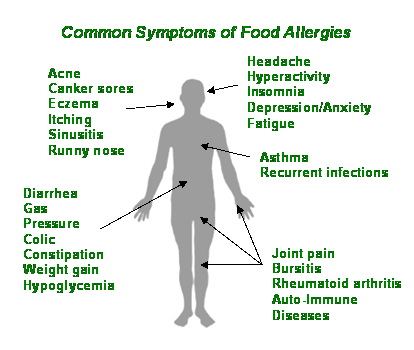
A food allergy is a reaction by the body’s immune system. When a person is sensitive to a food, such as peanuts, the immune system overreacts when the person comes in contact with that food.
True food allergies are quite rare, affecting only about 1 % of adults and about 5% of children.
Food Allergy or Food Intolerance?
 Many people think they have a food allergy, but what they really have is a food intolerance, which is a problem in the digestive tract and does not involve the immune system.
Many people think they have a food allergy, but what they really have is a food intolerance, which is a problem in the digestive tract and does not involve the immune system.
In someone with a food intolerance, either the food irritates the digestive tract or the body is unable to digest that food properly.
While the symptoms of food allergies and food intolerances are often similar, there are important differences between them as well.
Eating even a tiny amount of a food can trigger an allergic reaction, and the reaction will happen every time the person eats that food.
On the other hand, a food intolerance may not cause a reaction unless a large amount of the food is consumed.
For example, in someone with lactose intolerance drinking a cup of coffee with a small amount of milk in it may not cause a problem, but that same person might become sick after drinking a whole glass of milk.
The foods that most commonly trigger allergies are:
- cow’s milk
- eggs
- fish (such as bass, cod, and flounder)
- shellfish (such as crab, lobster, shrimp)
- peanuts
- tree nuts (such as almonds, cashews, hazelnuts, pecans, and walnuts)
- wheat
- soy
Symptoms of Food Allergies
Food allergy symptoms usually develop within an hour of eating the food, sometimes within minutes, and they can range from mild and annoying to frightening and life-threatening. People who are especially sensitive may have a reaction from simply touching the food or breathing in particles of it.
Symptoms of a food intolerance may be extremely uncomfortable, but they are typically less serious than the symptoms of a food allergy.
In severe cases of food allergy, the person may suffer from a life-threatening reaction known as anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock. This dangerous reaction can cause:
- tightening of the airways, including a swollen throat that causes breathing difficulties
- shock, with a severe drop in blood pressure
- rapid pulse
- dizziness, light headedness, or loss of consciousness.
Treatment of Food Allergies
These are warning signs of a serious problem and require immediate medical attention. There is a medication (epinephrine) that people with serious allergies should carry at all times.
It comes in a self-injecting device, and anyone who has food allergies or knows someone who does should know how to use the device. This can, quite literally, be a life saver. Even if the reaction is controlled quickly, immediate medical attention is still necessary. A single injection is not always enough to completely control the reaction.
People with severe allergies should also wear medical identification jewelry. During a severe reaction a person may not be able to speak, and this jewelry can identify the problem for emergency medical personnel so that the proper treatment can be given quickly.
When a child has a food allergy, the parents must take special precautions. Make sure that all caregivers (including family members, teachers, babysitters, and the parents of the child’s friends) all know how to use the epinephrine injection device. Older children should learn to use the device themselves.
Parents must also impress on children how important it is not to eat the food they are allergic to. Young children should be instructed never to eat food given to them by anyone other than a family member. Older children should be instructed to ask about any food someone gives them and to make sure the person giving them the food knows about their allergy and how serious it is.